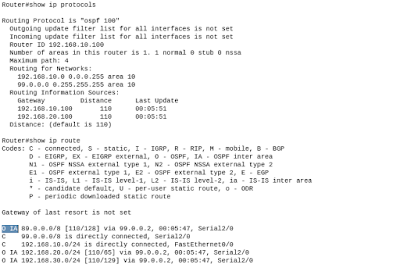
Open Shortest Path First:
- It is a link state protocol
- Standard protocol
- It uses shortest path first or dijkistra algorithm
- Unlimited hop count
- Metric is cost (cost=10^8/B.W.)
- Administrative distance is 110
- It is a classless routing protocol (carry subnet mask
information and supports VLSM)
- It supports equal cost load balancing
OSPF process in sever stages:
01 Down stage
02 Init stage
03 Two-way stage
04 Exstart stage
05 Exchange stage
06 Loading stage
07 Full stage
OSPF Router-ID:
It is used to identify the router inside the OSPF database.
OSPF identify using same ID in all directions.
It uses highest IP address of all active physical interface
by default.
OSPF Tables:
Neighbor table – It contains list of directly
connected routers
Database table –
It referred to as LSDB (Link state database)
It contains information about all the possible routes to the
network with in the area
Routing table – It contains best route to the
destination
Advantages of OSPF:
Open standard
No hop count limitations
Faster convergence
Disadvantages of OSPF:
Consume more CPU resources
Complex design rules